EEHA – Electrical Equipment in Hazardous Areas
In electrical engineering a hazardous area is a place where a fire or explosion hazard may exist due to:
- flammable gases or vapours
- combustible dusts or ignitable fibres
which may be present in the air in quantities sufficient to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures.
Where are hazardous areas found?
Places like oil refineries, chemical plants and sewerage treatment plants are areas where hazardous gas vapours may be present; however, many companies don’t realise dust can also create hazardous areas in places such as food and beverage manufacturers, plastics factories and recycling operations.
Typical industries with hazardous areas:
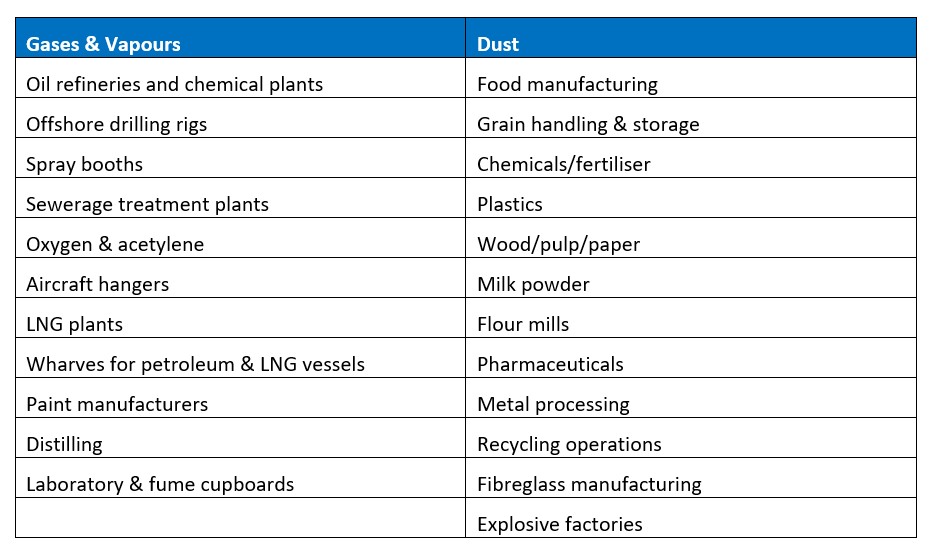
Due to the risks associated with these hazardous areas, staff accredited with an EEHA qualification need to take responsibility for installing and maintaining any electrical equipment in these areas. The electrical equipment installed in these areas must also be specifically designed and tested to ensure it doesn’t cause an explosion either due to arcing or its high surface temperature.
While the development of technology and rigorous health and safety practices have improved the safety of today’s manufacturing operations; the inherent risk of combining electrical equipment and hazardous areas still exists. Therefore, staff working in these areas must carry EEHA certification.
EEHA qualified people can:
- identify hazardous areas
- understand hazardous area drawings
- understand explosion protection techniques
- are skilled in equipment installation in these areas
- are familiar with procedures for breakdowns and the maintenance of equipment in hazardous areas
- ensure all hazardous area dossiers are updated.
At EAS we have team members certified in EEHA and can assist you with the full process of installing or maintaining electrical equipment in a hazardous area.
Electrical equipment in hazardous areas
Explosive atmospheres have different chemical properties that affect the likelihood and severity of an explosion. Every substance has a differing combination of properties, but it has been found that they can be ranked in similar ranges, simplifying the selection of equipment for hazardous areas. This table shows the different classifications applied to electrical equipment.
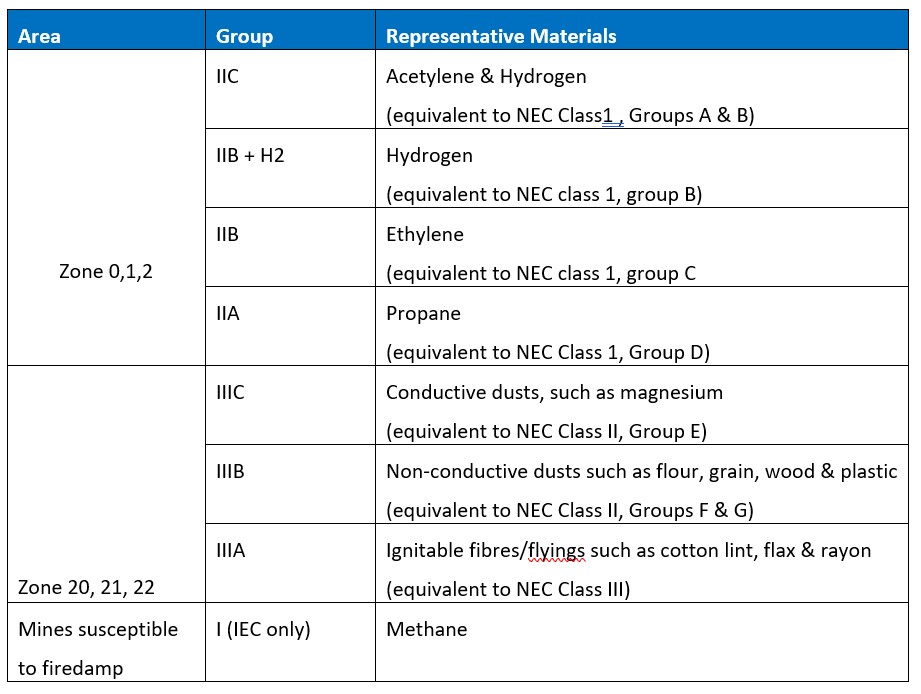
Another important consideration when selecting equipment to be used in a hazardous area is its temperature classification. The surface temperature of electrical equipment which may be exposed to the hazardous atmosphere needs to be tested to ensure it does not exceed 80% of the auto ignition temperature of the specific gas or vapour in the area it is being used. The different temperature tiers are:
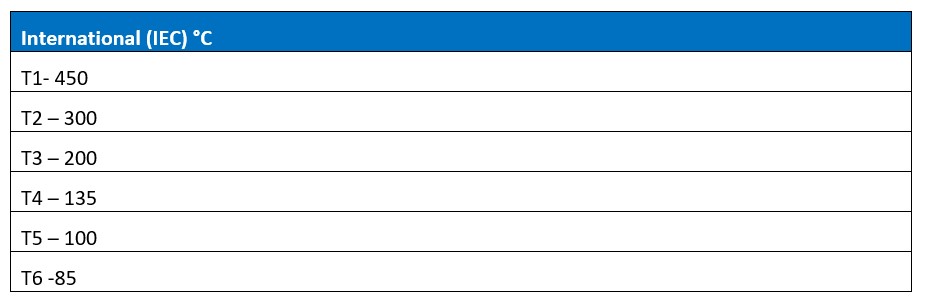
All electrical equipment installed in a hazardous area should carry ICE/Ex certification which states what zone it can be used in and the temperature it has been rated to.

When installing electrical equipment in hazardous areas it is essential that:
- Checks are done of existing hazardous area inspections and drawings.
- A hazardous area drawing and dossier is created, if it does not already exist.
- All electrical equipment to be installed carries ICE/Ex certificate.
- Installation of new equipment is carried out by EEHA qualified electricians.
EAS can coordinate the whole process of maintaining and installing electrical equipment in hazardous areas for you. From inspections, drawings, installation, testing and certification. EAS can deliver you a complete turnkey solution.
If you’re planning a new equipment installation in your plant, which is classed as a hazardous area, or need to conduct maintenance on equipment in hazardous areas; get in touch with the EAS team today on 07 834 0505.
When it comes to safety precautions and installation practices in hazardous areas, our team does not cut corners.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!