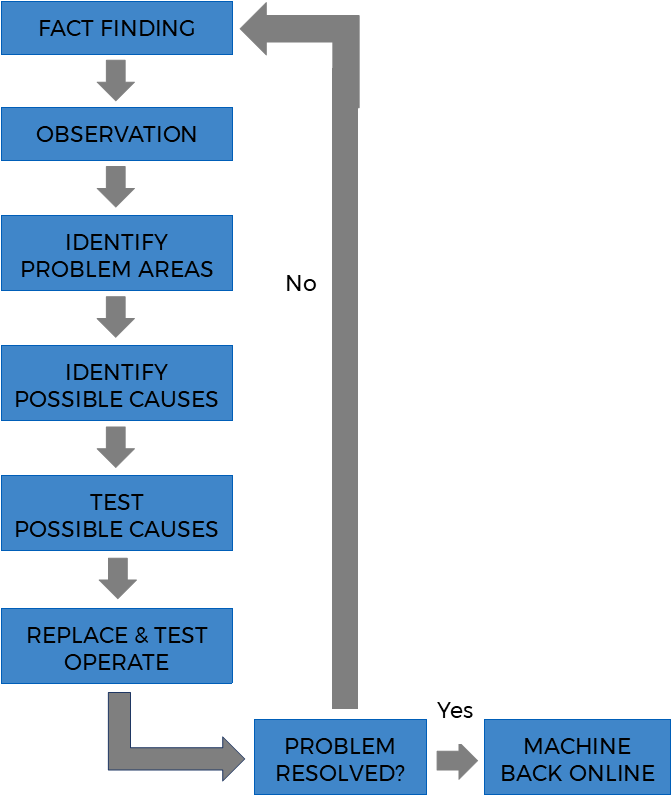
A motor is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to power a range of processes from simple functions like powering a fan to industrial operations such as pumps, conveyors or agitators.
Motors differ according to their power type (AC or DC) and their method of generating rotation. AC motors are used to drive complex and more fragile equipment, whereas DC motors usually power heavier equipment that needs easier maintenance and operation controls. AC motors can also provide higher levels of torque, which means they are often considered more powerful than DC motors.
There are various types of both AC and DC motors.
MOTOR TYPES – DC MOTORS
Brushed DC motors
Brushed DC motors have a simple design and are easy to control. While they are used in a range of consumer goods such as small appliances, they can also be suitable for industrial applications where high torque is required. For example, dispensing equipment used in the medical and packaging fields.
The disadvantage of brushed DC motors is that the brushes and commutators tend to wear relatively quickly. Their continuous contact means they require frequent replacement and periodic maintenance.
Brushless DC Motors:
As the name suggests, Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) do not use brushes. Instead, the rotor is a permanent magnet. The coils do not rotate but are instead fixed in place on the stator. Because the coils do not move there is no need for brushes and a commutator.
The permanent magnet rotates by changing the direction of the magnetic fields generated by the surrounding stationary coils. To control the rotation, you adjust the magnitude and direction of the current into these coils.
Brushless DC Motors are used in industrial applications where precise motion control and stable control are critical. These include:
- Linear motors
- Servomotors
- Actuators for industrial robots
- Extruder drive motors
- Feed drives for CNC machine tools
Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors are driven by pulses. They rotate through a specific angle or step with each pulse. Because the rotation is precisely controlled by the number of pulses received, these motors are widely used to implement positional adjustments.
Examples of the types of industrial applications they may be used for include:
- printing presses
- medical imaging machinery
- CNC milling machines.
MOTOR TYPES – AC MOTORS:
Induction Motors:
An induction motor is an AC electric motor. The electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained via electromagnetic induction from the rotating magnetic field of the stator winding.
Induction motors are the most frequently used type of motor. They are used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, with over 80% of all motors being induction motors.
Induction motors are also known as Asynchronous Motors. This is because an induction motor always runs at a slower speed than synchronous speed. The speed of the rotating magnetic field in the stator is called synchronous speed.
There are two main types of AC induction motor: single-phase and three-phase.
Single-phase induction motors are used extensively for smaller loads, such as household appliances like fans. While these motors have traditionally been used in fixed-speed applications, they are increasingly being used with variable-frequency drives (VFD).
Single-phase Induction Motors are used for:
- Pumps
- Compressors
- Small fans
- Drilling machines
Industrial applications generally require three-phase motors. A three-phase AC motor has three main stator windings and operates on three-phase AC power. Three-phase motors are self-starting and can produce a large initial torque. AC induction motors for industrial applications range in size from 1 to 100,000 hp.
Most three-phase motors have squirrel cage rotors, but they can also have wound rotors. Squirrel cage motors are more widely used as they have a simple design and rugged construction. This rugged construction means they require little maintenance which makes them a popular choice for domestic and industrial appliances.
Three Phase Induction Motor are used for:
- Lifts
- Cranes
- Hoists
- Large capacity exhaust fans
- Driving lathe machines
- Crushers
- Oil extracting mills
- Textile and etc.
Synchronous Motors:
In synchronous AC motors the rotor rotates in sync with the excitation field. The magnetisation of the rotor is produced by a permanent magnet in brushless designs or by windings with an AC current supplied through slip rings or brushes.
These motors maintain a constant speed at all loads. When the load exceeds the rated load, the motor ‘pulls out’ of synchronism and will stop operating. Synchronous motors are suitable for precision drives where accurate speed control is required.
The advantages of the synchronous motor are the ease with which the power factor can be controlled and the constant rotational speed of the machine, irrespective of the applied load.
Synchronous motors are used in:
- Belt driven reciprocating compressors
- Centrifugal pumps
- Various industrial mills
WHAT TO CONSIDER WHEN PURCHASING A MOTOR:
There are many aspects to consider when selecting an industrial motor. These include:
- The industrial application
How the motor will be used and any special considerations such as the physical space in which the motor needs to operate.
- Current:
Current is what powers the motor and too much current will damage the motor. For DC motors both operating and stall current are important.
- Voltage:
The voltage rating of a DC motor indicates its most efficient voltage while running. If too few volts are applied the motor will not work, whereas if too many volts can short windings resulting in power loss or complete destruction.
- Torque:
Operating and stall values also need to be considered with torque. Operating torque is the amount of torque the motor was designed to give and stall torque is the amount of torque produced when power is applied from stall speed.
- Velocity:
The general rule is that motors run most efficiently at the highest speeds, but it is not always possible if gearing is required. Adding gears will reduce the efficiency of the motor, so you need to consider speed and torque reduction as well when selecting the appropriate motor.
- Environment:
Most motors are designed to work in clean, dry, room temperature environments. If the motor is likely to be exposed to dust or water contamination or will be required to run at high temperatures than the motor options will be more limited.

Other considerations also include
- Does the application require a constant or variable speed?
- Is position control required for the application?
- What is the load and is it continuous or intermittent duty?
Selecting, installing, and maintaining the right motors in your company’s facilities and equipment is an essential step to ensuring uninterrupted operation and production.
Electrical & Automation Solutions (EAS) can provide you with advice on the right motor for your process as well as provide you with ongoing maintenance and service to ensure they continue to run in top notch condition – get in touch today!